Streamlining Excellence: Exploring the Power of Lean Six Sigma
In a world where efficiency and quality are paramount, organizations constantly seek ways to enhance their processes. lean six sigma, a fusion of two powerful methodologies—Lean and Six Sigma—has emerged as a guiding light in process improvement. In this blog, we will delve into the world of Lean Six Sigma, its core principles, methodologies, and the remarkable benefits it brings to organizations striving for excellence.
Understanding Lean Six Sigma
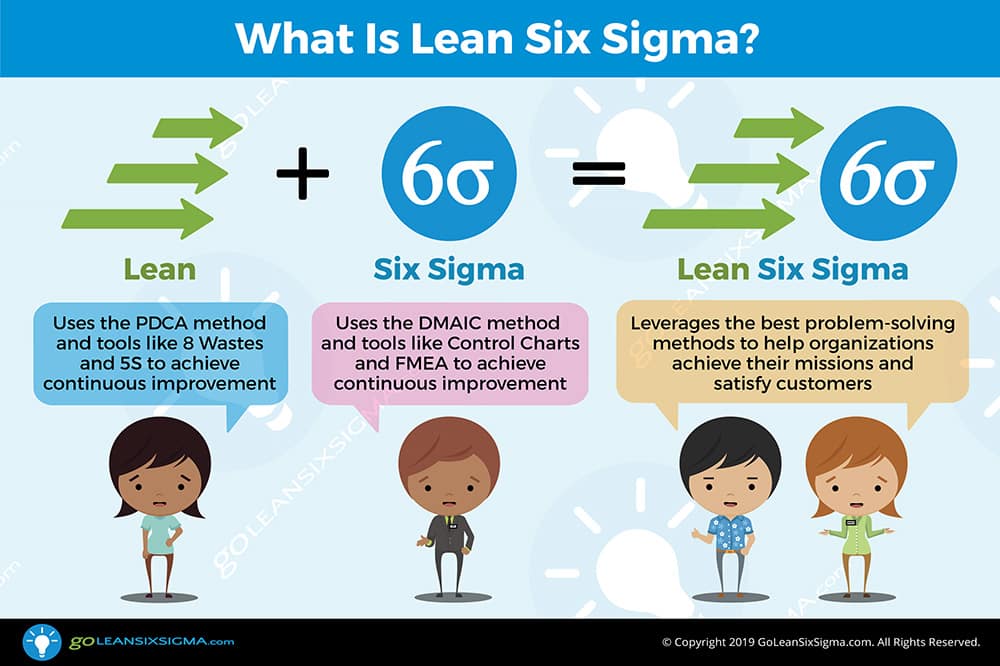
Lean Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology designed to improve processes by reducing waste and defects while simultaneously increasing customer satisfaction. It combines the efficiency-focused principles of Lean with the defect-reduction strategies of Six Sigma, creating a holistic approach to process improvement.
Key Principles of Lean Six Sigma
- Customer Focus: Lean Six Sigma begins with a relentless focus on understanding and meeting customer needs, aiming to provide products and services that consistently exceed expectations.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Data is the bedrock of Lean Six Sigma. Organizations collect, analyze, and utilize data to identify problems, measure process performance, and make informed decisions.
- Continuous Improvement: A commitment to ongoing improvement is at the heart of Lean Six Sigma. Organizations strive for perfection by relentlessly eliminating waste and reducing defects.
- Process Efficiency: Lean principles emphasize streamlining processes by eliminating non-value-added activities, reducing lead times, and optimizing resource utilization.
- DMAIC and DMADV: Lean Six Sigma uses two primary methodologies—the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) for process improvement and DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify) for designing new processes or products.
Phases of DMAIC
- Define: Clearly define the problem, project scope, and customer requirements.
- Measure: Collect data to measure the current process performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Analyze: Analyze data to uncover root causes of defects or inefficiencies.
- Improve: Develop and implement solutions to address identified issues and optimize the process.
- Control: Establish controls to maintain the improved process performance over time.
Benefits of Lean Six Sigma
- Enhanced Efficiency: By eliminating waste and streamlining processes, organizations achieve higher efficiency, lower lead times, and reduced operational costs.
- Improved Quality: The reduction of defects leads to higher product and service quality, resulting in increased customer satisfaction.
- Cost Reduction: Lean Six Sigma helps reduce costs by identifying and eliminating non-value-added activities and inefficiencies.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations that embrace Lean Six Sigma gain a significant competitive edge in their industries.
- Cultural Transformation: Lean Six Sigma fosters a culture of continuous improvement, teamwork, and data-driven decision making throughout the organization.
Challenges in Implementing Lean Six Sigma
Implementing Lean Six Sigma successfully may encounter challenges such as resistance to change, lack of data, and the need for comprehensive training. However, these hurdles can be overcome with strong leadership commitment and dedicated efforts.